Healthcare Interoperability – Privacy & Security
The world of Healthcare has drastically changed in the recent past with the incorporation of IT into Healthcare services. It has completely transformed the way in which healthcare data were traditionally shared, exchanged or interchanged. Today, we see a wide diversity in the way information is created, gathered, Processed and transmitted; and all this happening due to the adoption of IT in healthcare.
Basically, the reliance of healthcare and the associated industry on technology is fuelling the conversion of non-electronic data into electronic data to support the underlying varied technology platforms. In the process of providing the most technologically advanced, quality and value based healthcare service; there is huge demand for access to patient data from many disparate systems. The outcome? It is a composite IT environment, having a combination of legacy systems, on-premises systems and cloud systems.
What is Healthcare Interoperability?
Now let’s have a look of at the world of healthcare interoperability, which is making all this possible.
Interoperability is a uniform movement of healthcare data from one system to another, so that the clinical and operational purpose of the data is preserved and unaltered. In other words, it’s the ability of data to travel quickly and accurately from one healthcare venue to another. Accurate patient information can facilitate the right diagnosis and the right medication while avoiding tragic, avoidable errors.
It is about transforming the backbone healthcare information system into secure interoperable networks.
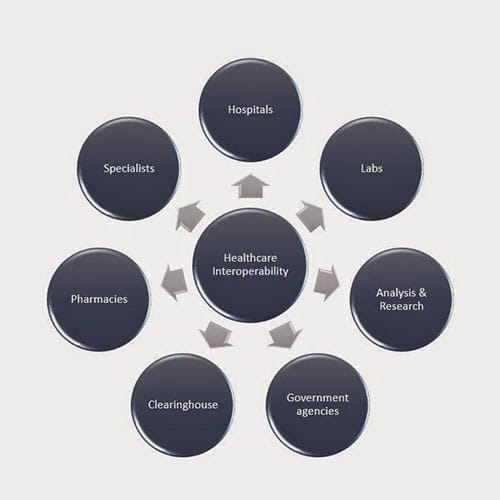
Imagine a patient visiting a physician for treatment where health records are initially created. The physician’s electronic health records can be used by doctors, hospitals, pharmacies, health plan and above all, the most important members of the team – Patients. All these pieces of information have to be together so that they can be shared across different healthcare settings such as doctor’s offices, and hospitals.
To achieve this, it is necessary to move from paper based health records to electronic ones. Each new piece of health information can connect to other pieces of health information. Patient health information should be made available when and where needed through healthcare interoperability. This can save time, money and above all, Human Lives.
Since the HITECH act was passed in 2009, electronic health record adoption has more than doubled in office practices and more than quadrupled in hospitals. Clear standards have been developed to make sure systems communicate with each other in a common language that they all understand. Ultimately, it is choosing the right balance between privacy and security.
Addressing Security and Privacy:
Security and privacy should be addressed from the start of any interoperability program. No one would be willing to go for wrong treatment because of lack of integrity of data. No one would be willing to disclose their sensitive clinical data to unwanted personnel because of confidentiality failure. And No one would be willing to suffer because of lack of availability of information at a critical time of treatment. Security and privacy program in interoperability solutions must address the following foundation elements to be successful.
- Security risk assessment: Having a risk-centric approach will surely benefit in concentrating on the weak areas and it will give a strategic direction for further IT investments.
- External communication: Encrypt data flowing through external/public networks. That doesn’t mean data is fully secure and un-alterable while in the internal network.
- Education and training: Technology will do its job. But avoiding human errors through appropriate training will surely create a sense of responsibility amongst the workforce.
- Vulnerability testing: The ever growing threat landscape will always haunt of the upcoming vulnerabilities. Get your systems tested!
- Security event handling: Yes! Reporting and handling that security incident timely will restrict further damage.
- Metrics and monitoring: Do not ignore those alerts raised by the monitoring system. Believe in numbers to rely that information systems are functioning, secure and supportive of end objectives.
- Audits and assessment: Having your environment regularly tested by a third party or internal auditors will help in maintaining not just compliance but holistic security.
- Security built into product development: What can be better than addressing security right from the inception and carrying it over the entire product development life cycle. It will benefit in building a robust and reliable product.
Source: http://healthit.ahrq.gov/
It is expected that the revolutionary form of health record will enhance healthcare and bring in flexibility and accessibility with reduced cost. But, at the same time, care needs to be taken to ensure sensitive health data does not land in the wrong hands. Along with the technological evolution of the healthcare industry, security and privacy needs to be addressed with equal enthusiasm. After all, it is the individual health data of which confidentiality, integrity and availability should be maintained with the highest level of security considering the criticality of health data.
 USA
USA India
India APAC
APAC Middle East
Middle East Global
Global

 Facebook
Facebook Linkedin
Linkedin  X
X Youtube
Youtube