Zeoticus 2.0 Ransomware – All You Need to Know

- The Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware can execute payloads offline without any C2 (Command & Control) connectivity.
- The new version of Zeoticus ransomware has adopted rapid encryption algorithms for both symmetric and asymmetric sides.
With the Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware even more top-of-mind, businesses are taking preventive steps to mitigate any risks. But incident response and threat analysis teams are not finding it easy to get rid of the Zeoticus 2.0 infection. Why? What to do about it? Get your questions answered.
What is Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware | The big picture
The versatility and effectiveness of the ransomware has underlined the increasing importance of attack prevention. Despite many Zeoticus events that have occurred in the year 2020, and contrary to its predecessor, the new Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware executes payloads without connecting to any C2 (Command and Control) channel. It executes fully offline without the need of receiving any commands from a remote server.
In the early 2020, this ransomware emerged for sale as ransomware-as-a-service in numerous underground forums and markets. Initially, it was offered as a full custom build. According to the developers, Zeoticus 2.0 is Windows-specific and can operate on all supported versions of Windows.
From 1.0 to Zeoticus 2.0 | The evolving menace
In December 2020, samples of Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware came to notice by multiple researchers and security vendors. After analysis, it was found that most of the updates in the second version of the Zeoticus ransomware were primarily focused on speed and efficiency. The symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms were chosen based on their speed (e.g., Poly1305 is used for signing the primary encryption key rather than the usual SHA1).
Indications have showed that the ransomware can even operate on Windows XP and earlier versions. Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware has the capability to discover and infect remote drives. It can also terminate processes that could potentially interfere with the encryption process by the ransomware.
The Zeoticus group has taken a step further with the new version of the ransomware that uses ping utility to covers its track by deleting the specific binaries. The Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware has morphed from a relatively minor challenge to being a business and economic threat. It may sound honest, but it is already time for businesses to equip their IT teams with the knowledge and tools required to stop the evolving menace.
Execution and persistence of the Zeoticus 2.0
As soon as the Zeoticus 2.0 payload gets executed, the relevant files are identified using extensions. It is notable that the encryptable-extension list is fully customizable and in the control of the threat actors. After launching, the malware starts to replicate itself and copies appear in C:\Windows and %AppData%.
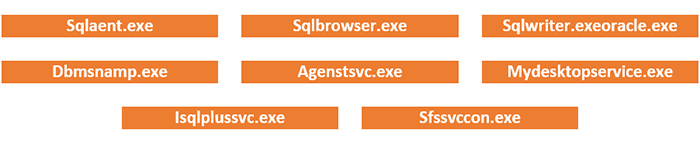
It then kills numerous running processes, which can potentially hinder its encryption, via task-kill.exe.
Following are some of the processes terminated by the ransomware:
Zeoticus uses the ping utility to redirect command output to >nul & del, which resultantly facilitate the deletion of its own binaries. The additional information about the local environment is gathered via a WMI query.
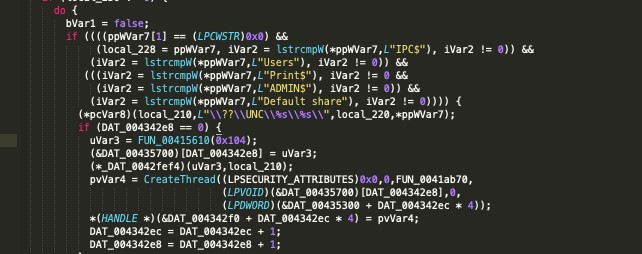
Source: https://labs.sentinelone.com/zeoticus-2-0-ransomware-with-no-c2-required/
To achieve persistence, the Zeoticus ransomware creates a registry run key, which is set to launch an instance of Zeoticus payload from the default directory of C:\Windows in registry locations \REGISTRY\USER\—-\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\
Encryption and ransom note of the Zeoticus 2.0
The ransomware uses both asymmetric and symmetric algorithms for encryption. XChaCha20 is utilized on the symmetric side, while the combination of Poly1305, XSalsa20 and Curve25519 is used for the asymmetric side. After the encryption process is completed, the files are modified with extensions that contain the email addresses of the adversaries and a string “2020END”, potentially a reference to the new year.
For example, a file called “1.jpg” was renamed to “1.jpg.6361383701972502380.outsourse@tutanota.com.2020END”, and “2.jpg” to “2.jpg.6361383701972502380.outsourse@tutanota.com.2020END”, and so on. What’s even more concerning, Zeoticus 2.0 has the capability of mounting a new volume which ultimately contain the ransom note. This is where the victims are instructed to contact the attacker via email to process the ransom payment in bitcoins.
Victims are informed to write an email to outsourse@tutanota.com or outsourse@cock.li and wait till the developers of the Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware to send payment information which is the price of a decryption software and instructions on how to pay for it.
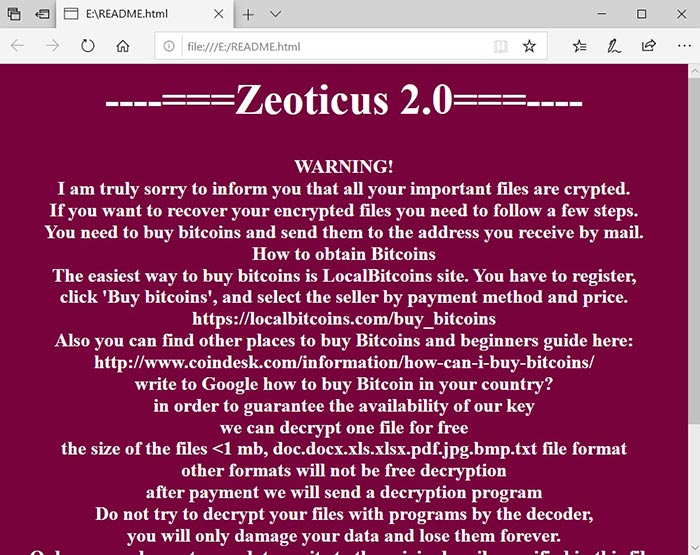
Source: https://labs.sentinelone.com/zeoticus-2-0-ransomware-with-no-c2-required/
Also, the ransomware drops a copy of the ransom note to the root of the system drive (e.g., C:\WINDOWS\README.html). The desktop background of the system is also changed to a ransom note in some versions of the Zeoticus ransomware.
Mitre Att&Ck
- Data from Local System
- Credentials from Password Stores
- Modify Registry
- Query Registry
- Remote System Discovery
- System Information Discovery
- Peripheral Device Discovery
- Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder
- Data Encrypted for Impact
How did the Zeoticus 2.0 ransomware infect your system?
Most of the ransomware infections are through spam mails, certain trojans, fake software updating tools, untrustworthy files, software download channels or use of unofficial software activation (cracking) tools. As soon as the user downloads and opens any malicious attachments, the payload gets triggered, and the computer gets infected by the malware. Certain trojans can cause chain infections such as installing additional malware.
Untrustworthy software download sources (such as torrent network) can also be used to distribute ransomwares. Typically, cyber criminals attempt to trick users into downloading such files by disguising them as legitimate.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) of Zeoticus 2.0
Email address:
- outsource@tutanota[.]com
- outsourse@cock[.]li
File names:
- README[.]html
Registry:
- \REGISTRY\USER\—-\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\ (set to launch Zeoticus from the Windows installation directory)
File hashes

How to remediate the Zeoticus 2.0?
- Critical data should be frequently saved in multiple backup locations.
- One backup should be kept offline at any time.
- Backups and incident recovery plans should be tested to ensure that data can be restored when needed.
- Always follow principle of least privilege (PoLP).
- Infected systems should be disconnected from the network and powered down as soon as the compromise is detected.
- Any user account credentials that could have compromised during the attack should be reset.
- Secure configurations need to be applied to all devices.
- Security updates should be applied on a regular basis.
- Tamper protection settings in security products should be enabled where applicable.
- Obsolete platforms should be segmented from the rest of the network.
- IT usage policies should be reinforced by regular awareness training to ensure that users never open unsolicited links or attachments.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and lockout policies should be enforced especially for administrative accounts.
- Remote administration services should use strongly encrypted protocols and only accept connections from authorized users or locations.
- Systems should continuously be monitored, and unusual activity should be proactively investigated, so that a compromise of the network can be detected as early as possible.
The bottom line
Prevention of ransomware attacks is more important than ever because of the difficulty of recovering from such attacks. Organizations are encouraged to review their security posture and take all necessary actions to enhance their protection and reduce the overall attack surface. It is important to educate end users on the methodologies used by the threat actors and encourage them to proactively report any suspicious activity they observe.
New incoming ransomwares doesn’t need to be as dreadful as it seems. Finally, as you keep adding to your threat hunting and incident response capabilities, the risk level from ransomware attacks decreases substantially.
 USA
USA India
India APAC
APAC Middle East
Middle East Global
Global

 Facebook
Facebook Linkedin
Linkedin  X
X Youtube
Youtube